1
/
of
1
Human Beta-2-Glycoprotein 1 (APOH) ELISA Kit
Human Beta-2-Glycoprotein 1 (APOH) ELISA Kit
This ELISA kit is designed to detect Human Beta-2-Glycoprotein 1 (Human APOH). The assay plate has been pre-coated with mouse anti-Human Apolipoprotein H monoclonal antibody. When the sample containing Apolipoprotein H is added to the plate, it binds to the antibodies coated on the wells. Then, a horseradish peroxidase conjugated mouse anti-Human Apolipoprotein H Antibody is added to the wells and binds to Apolipoprotein H in the sample. After washing the wells, substrate solutions are added, and the color intensity is directly proportional to the amount of Human Apolipoprotein H present. The reaction is stopped by adding an acidic stop solution, and the absorbance is measured at 450 nm.
Catalog No:
BPE188
Regular price
$624.00 USD
Regular price
$480.00 USD
Sale price
$624.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
2 weeks
Couldn't load pickup availability
Product Details
Species Reactivity
Human
Sensitivity
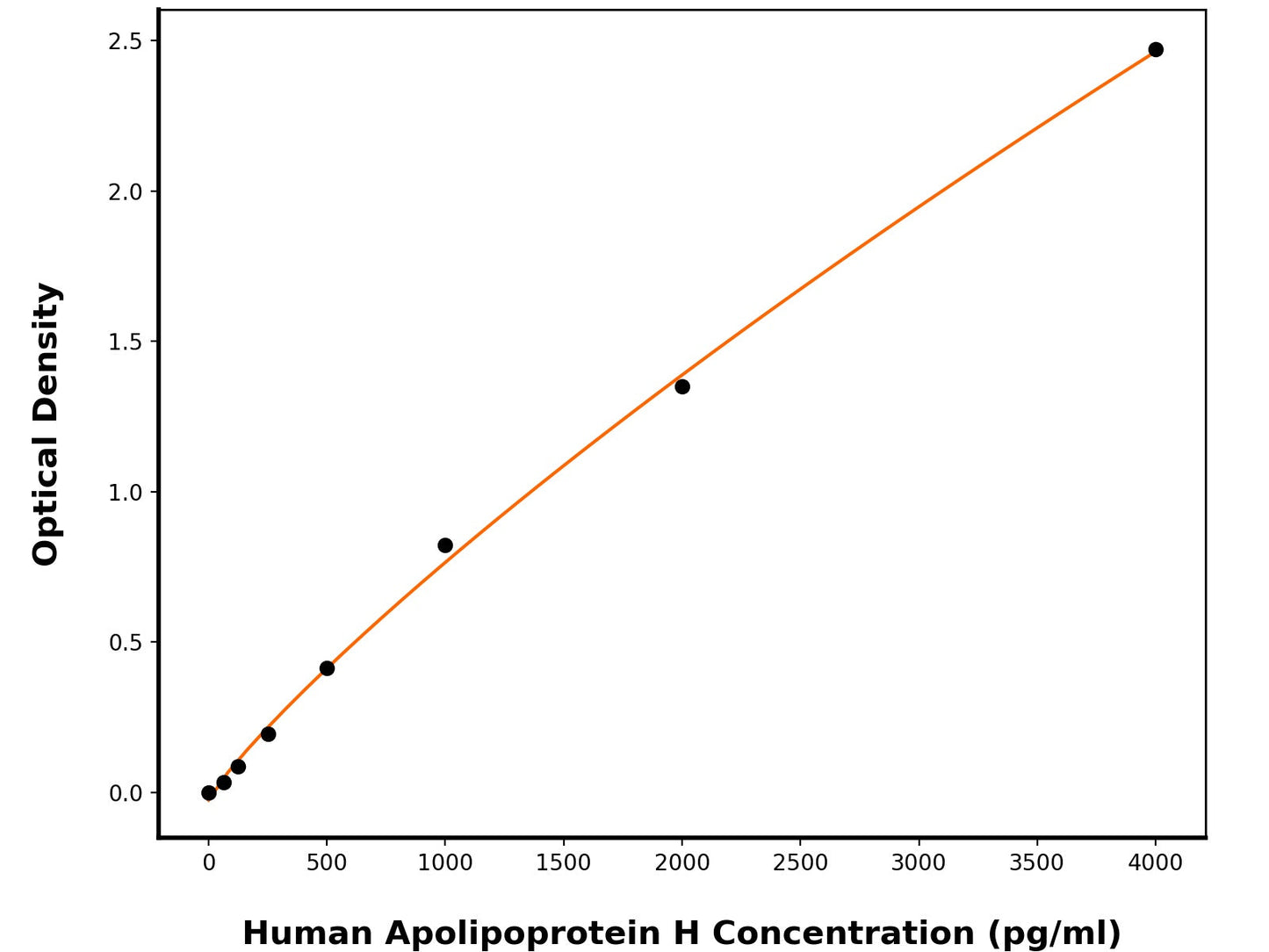
11.68 pg/mL
Detection Range
62.5-4000 pg/mL
Sample Type
Serum, plasma, cell culture supernates
Incubation(s)
3.5 hour(s)
Research Areas
Cardiovascular, Signal Transduction
Background
Apolipoprotein H (APOH), also known as Beta-2-glycoprotein 1, Activated protein C-binding protein, B2GPI, and B2G1, is a glycoprotein synthesized by liver cells and it is present in the blood associated with plasma lipoproteins. It is an essential cofactor for the binding of certain antiphospholipid antibodies (APA) to anionic phospholipid. APOH binds to various kinds of negatively charged substances such as heparin, phospholipids, and dextran sulfate. APOH may prevent activation of the intrinsic blood coagulation cascade by binding to phospholipids on the surface of damaged cells. APOH appears to completely inhibit serotonin release by the platelets and prevents subsequent waves of the ADP-induced aggregation. The activity of APOH appears to involve the binding of agglutenating, negatively charged compounds, and inhibits agglutenation by the contact activation of the intrinsic blood coagulation pathway. APOH causes a reduction of the prothrombinase binding sites on platelets and reduces the activation caused by collagen when thrombin is present at physiological serum concentrations of APOH suggesting a regulatory role of APOH in coagulation. APOH plasma concentrations are strongly associated to metabolic syndrome alterations and vascular disease in type 2 diabetic and could be considered as a clinical marker of cardiovascular risk. APOH is found on several classes of lipoproteins, and is involved in the activation of lipoprotein lipase in lipid metabolism. This single-chain glycoprotein also has been implicated in several physiologic pathways including coagulation and the production of hypertension, which are related to the pathogenesis of primary cerebral hemorrhage (PICH).
Shipping Condition
Shipped on cold gel packs.
Storage Condition and Shelf Life
This product can be stored at 2-8C.
Analyte
Beta-2-glycoprotein 1
Regulatory Status
For Research Use Only