1
/
of
1
Human Delta-Like Protein 4 (DLL4) ELISA Kit
Human Delta-Like Protein 4 (DLL4) ELISA Kit
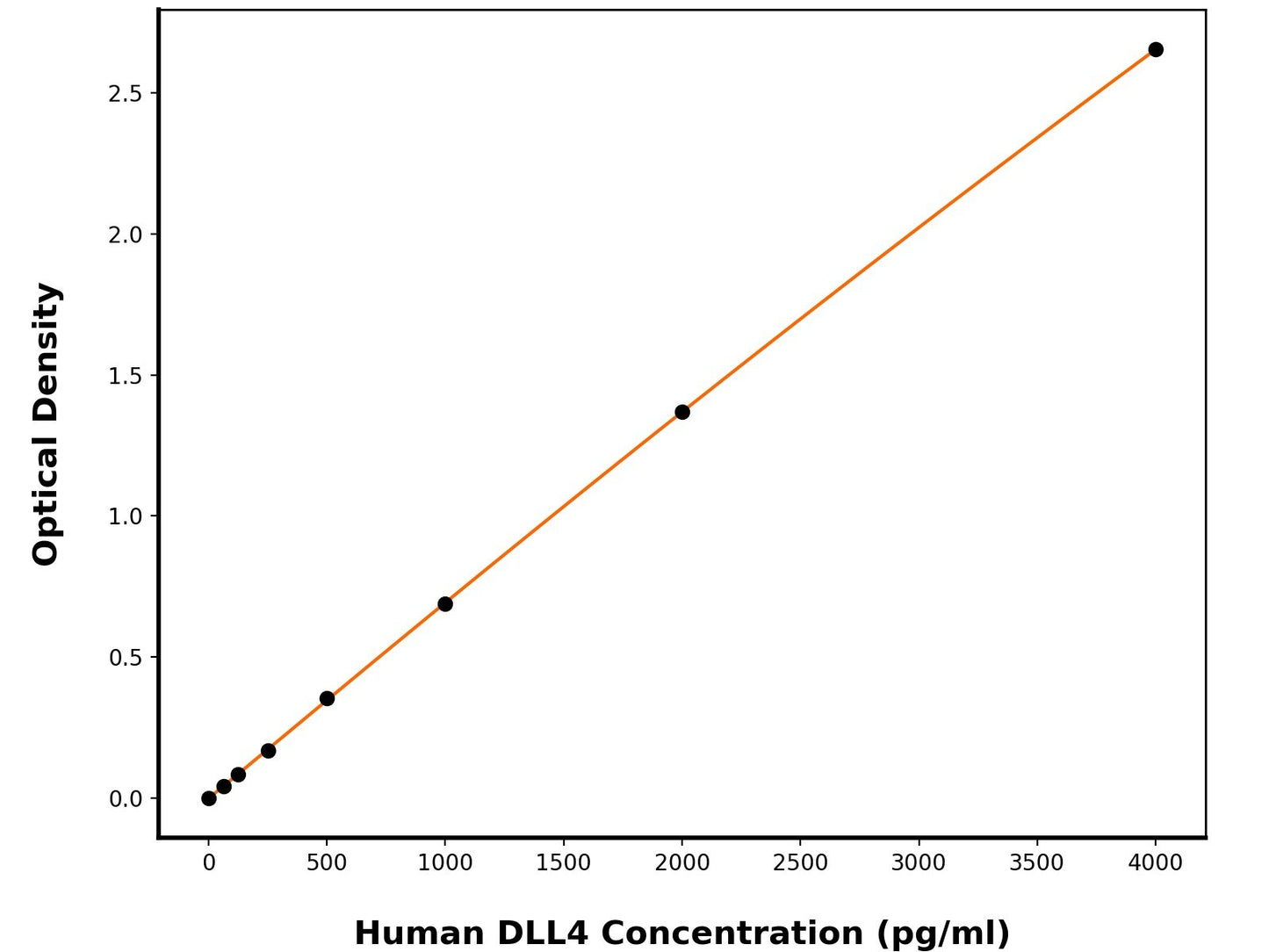
This ELISA kit is designed to detect Human Delta-Like Protein 4 (Human DLL4). The assay plate has been pre-coated with mouse anti-Human DLL4 monoclonal antibody. When the sample containing DLL4 is added to the plate, it binds to the antibodies coated on the wells. Then, a horseradish peroxidase conjugated mouse anti-Human DLL4 Antibody is added to the wells and binds to DLL4 in the sample. After washing the wells, substrate solutions are added, and the color intensity is directly proportional to the amount of Human DLL4 present. The reaction is stopped by adding an acidic stop solution, and the absorbance is measured at 450 nm.
Catalog No:
BPE036
Regular price
$754.00 USD
Regular price
$580.00 USD
Sale price
$754.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
2 weeks
Couldn't load pickup availability
Product Details
Species Reactivity
Human
Sensitivity
25 pg/mL
Detection Range
62.5-4000 pg/mL
Sample Type
Serum, plasma, cell culture supernates
Incubation(s)
3.5 hour(s)
Research Areas
Cancer, Cell Biology, Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling, Neuroscience
Background
Delta-like protein 4 (DLL4, Delta4), a type I membrane-bound Notch ligand, is one of five known Notch ligands in mammals and interacts predominantly with Notch 1, which has a key role in vascular development. Recent studies yield substantial insights into the role of DLL4 in angiogenesis. DLL4 is induced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and acts downstream of VEGF as a 'brake' on VEGF-induced vessel growth, forming an autoregulatory negative feedback loop inactivating VEGF. DLL4 is downstream of VEGF signaling and its activation triggers a negative feedback that restrains the effects of VEGF. Attenuation of DLL4/Notch signaling results in chaotic vascular network with excessive branching and sprouting. DLL4 is widely distributed in tissues other than vessels including many malignancies. Furthermore, the molecule is internalized on binding its receptor and often transported to the nucleus. In pathological conditions, such as cancer, DLL4 is up-regulated strongly in the tumour vasculature. Blockade of DLL4-mediated Notch signaling strikingly increases nonproductive angiogenesis, but significantly inhibits tumor growth in preclinical mouse models. In preclinical studies, blocking of DLL4/Notch signaling is associated with a paradoxical increase in tumor vessel density, yet causes marked growth inhibition due to functionally defective vasculature. Thus, DLL4 blockade holds promise as an additional strategy for angiogenesis-based cancer therapy.
Shipping Condition
Shipped on cold gel packs.
Storage Condition and Shelf Life
This product can be stored at 2-8C.
Analyte
Delta-like protein 4
Regulatory Status
For Research Use Only