1
/
of
1
Human Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) ELISA Kit
Human Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) ELISA Kit
This ELISA kit is designed to detect Human Parathyroid Hormone (Human PTH). The assay plate has been pre-coated with mouse anti-Human Parathyroid Hormone monoclonal antibody. When the sample containing Parathyroid Hormone is added to the plate, it binds to the antibodies coated on the wells. Then, a horseradish peroxidase conjugated mouse anti-Human Parathyroid Hormone Antibody is added to the wells and binds to Parathyroid Hormone in the sample. After washing the wells, substrate solutions are added, and the color intensity is directly proportional to the amount of Human Parathyroid Hormone present. The reaction is stopped by adding an acidic stop solution, and the absorbance is measured at 450 nm.
Catalog No:
BPE267
Regular price
$754.00 USD
Regular price
$580.00 USD
Sale price
$754.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
2 weeks
Couldn't load pickup availability
Product Details
Species Reactivity
Human
Sensitivity
56.92 pg/mL
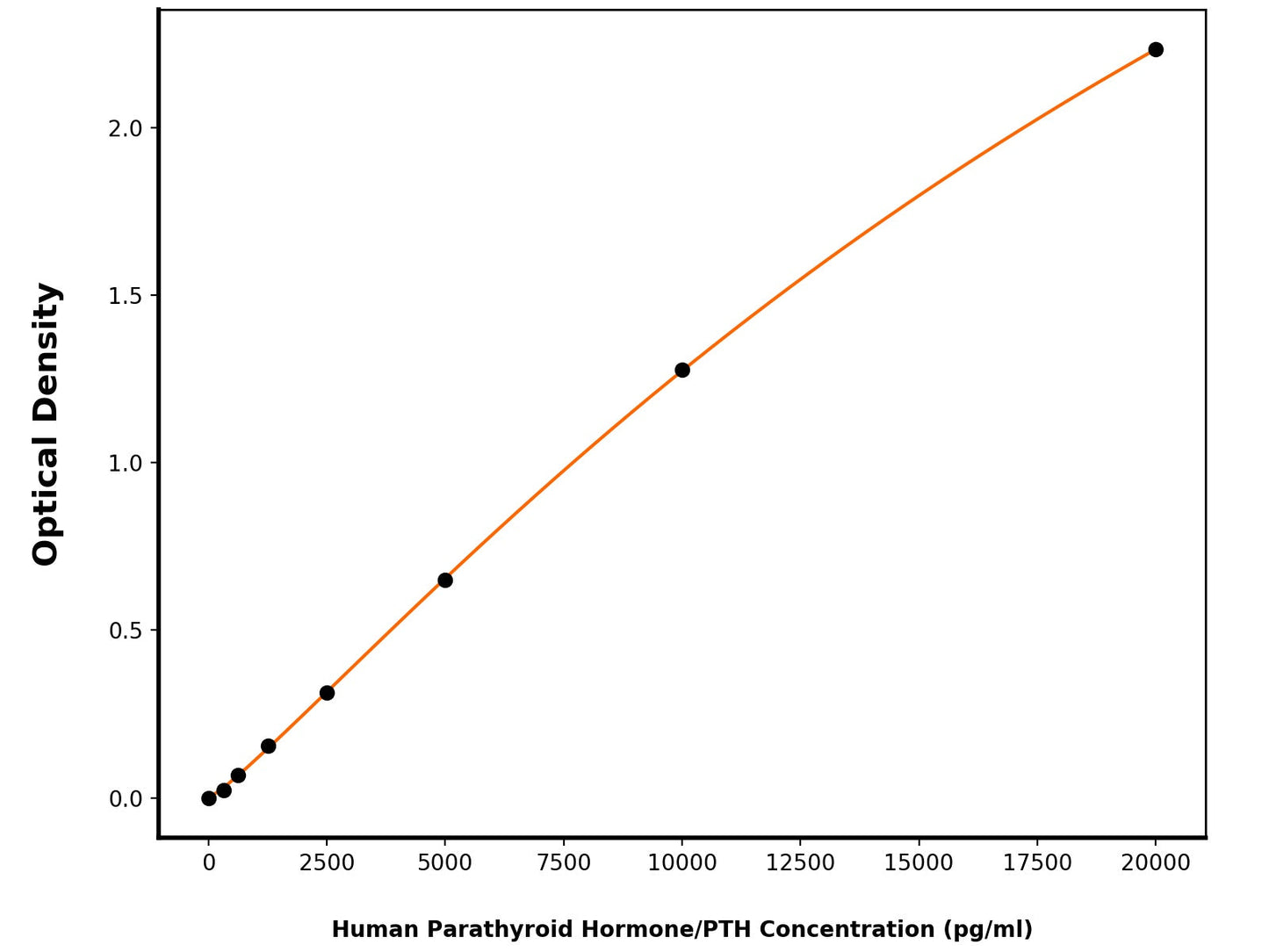
Detection Range
312.5-20000 pg/mL
Sample Type
Serum, plasma, cell culture supernates
Incubation(s)
3.5 hour(s)
Research Areas
Signal Transduction
Background
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), parathormone or parathyrin, is secreted by the chief cells of the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide. PTH elevates calcium level by dissolving the salts in bone and preventing their renal excretion. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) has been proved to play a pivotal role in maintaining myocardial contractility as well as effective natriuresis, and possible pathogenic mechanisms contributing to heart failure secondary to hypocalcemia and hypoparathyroidism. With the increased population of preosteoblastic lineages and the osteoblastic activation, Parathyroid hormone (PTH) drives anabolism in bone. Experiments have recently reported that PTH affects bone cells in a dual pathway - mediating osteoblastic (preosteoblastic) activities or osteocytic synthesis of sclerostin. Defects in PTH are a cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism (FIH), also called autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism or autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. FIH is characterized by hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia due to inadequate secretion of parathyroid hormone. Symptoms are seizures, tetany and cramps.
Shipping Condition
Shipped on cold gel packs.
Storage Condition and Shelf Life
This product can be stored at 2-8C.
Analyte
Parathyroid hormone
Regulatory Status
For Research Use Only